Exhibition UMBAU. Nonstop Transformation // April 10 - May 5, 2025 - Jiushi Art Salon Shanghai
Plaster casting facility of Staatliche Museen zu Berlin
gmp wins open competition for refurbishment and extension
In the open two-stage competition for the refurbishment and extension of the plaster casting facility of the Staatliche Museen zu Berlin (engl. Berlin State Museums), which had to meet listed-building standards, the design by architects von Gerkan, Marg and Partners (gmp) won first prize.

The plaster casting facility of the Berlin State Museums is the largest facility of this kind in the world. High-quality replicas of pieces of art from museum collections in Berlin and Europe have been produced here for over 200 years. This means that the plaster casting facility is not only a production facility but also boasts a large collection of historic molds and master models of art and cultural objects from all time periods and geographic regions.

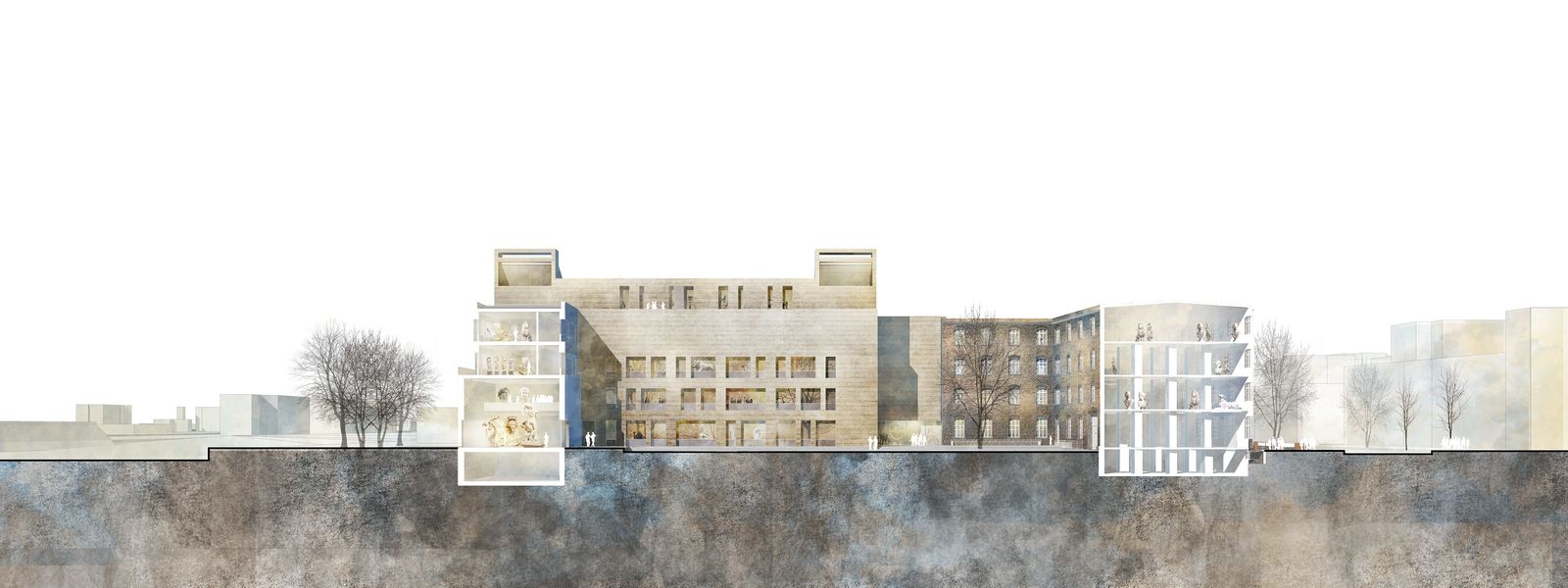
Owing to the current lack of space and the poor condition of the existing building it is now going to be fully refurbished and expanded with a new extension – growing from the current area of about 5,000 square meters to a total of about 13,000. Special requirements stipulated in the competition brief included sustainable and resource-efficient construction. To this end, a low-tech strategy had to be developed that prioritized robust, low-maintenance solutions over more high-tech technologies.

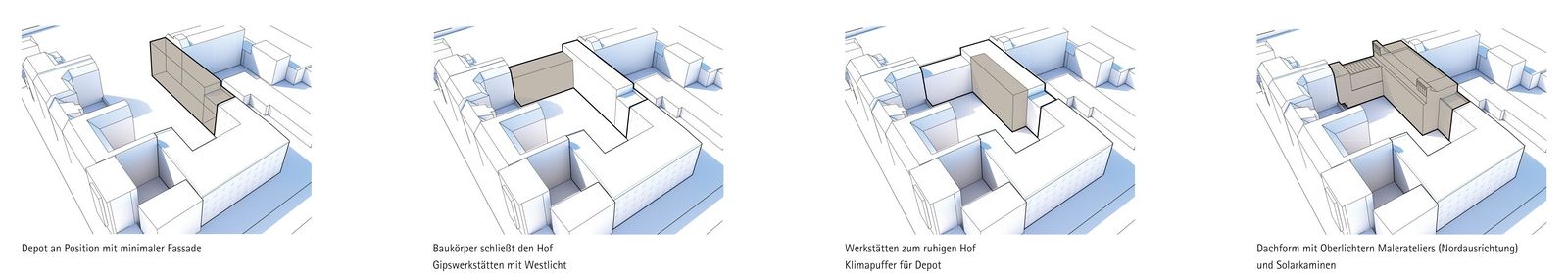
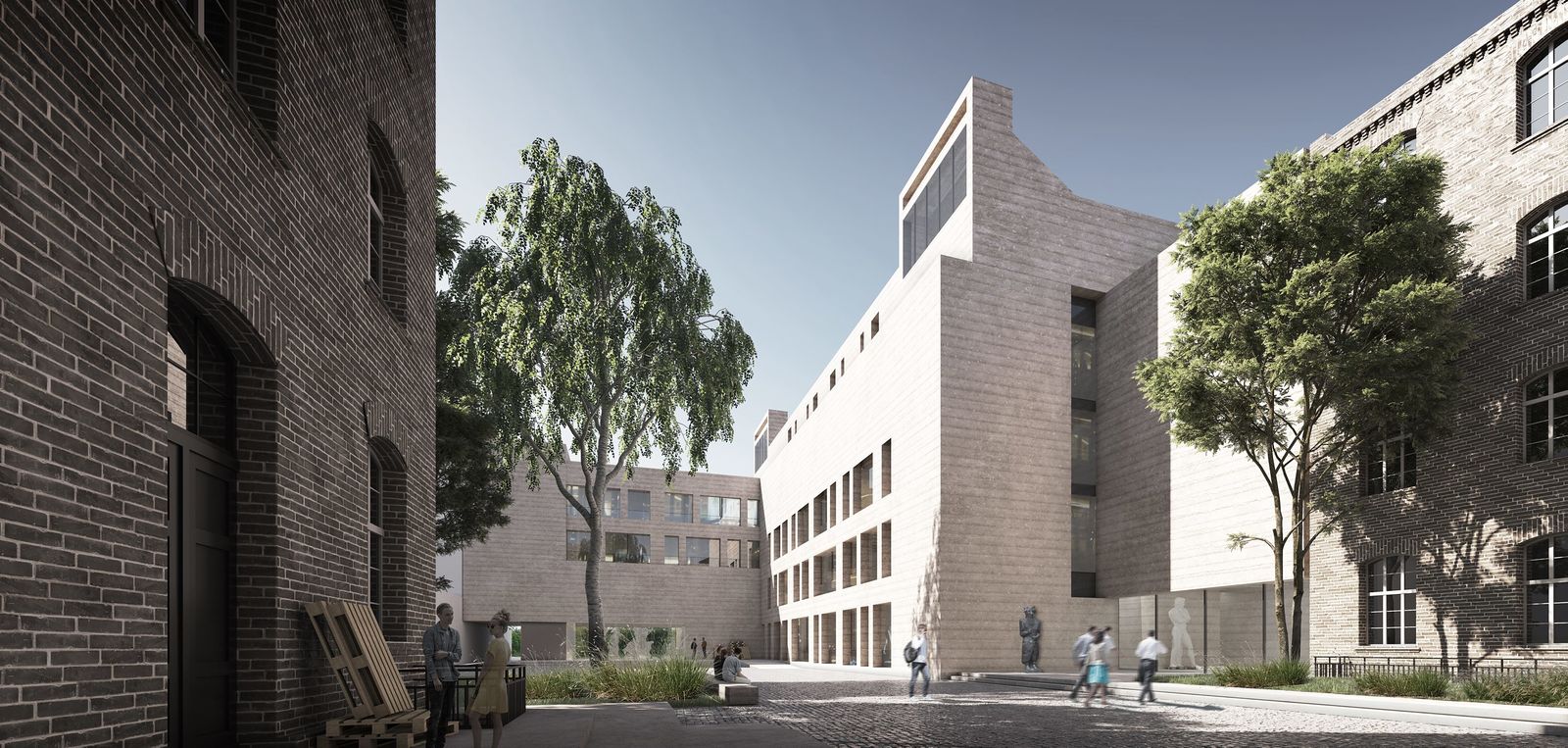
The extension building designed by gmp is connected to the existing facility to the north of the site. In terms of urban design, this arrangement provides a convincing solution as the new building resembles the existing facility in its overall volume and – with its L-shaped layout – also blocks off the site towards the west and the urban freeway. In this way, the neighboring residential buildings become part of the newly created urban inner courtyard, and an effective acoustic screening is achieved that blocks noise from the urban freeway and the railway track. In line with the planned low-tech strategy, the layout of functions within the building makes ideal use of the different climate and acoustic zones created.
The new building consists of a combination of monolithic insulating concrete walls with a floor/ceiling construction that is a modern and economic interpretation of the vault ceilings of the existing building. Natural background ventilation is provided without mechanical boosters, using ground heat exchangers and solar chimneys on the roof, thus optimally reducing the energy requirement. Mechanical devices to boost natural air exchange are only needed in a few areas with special requirements.
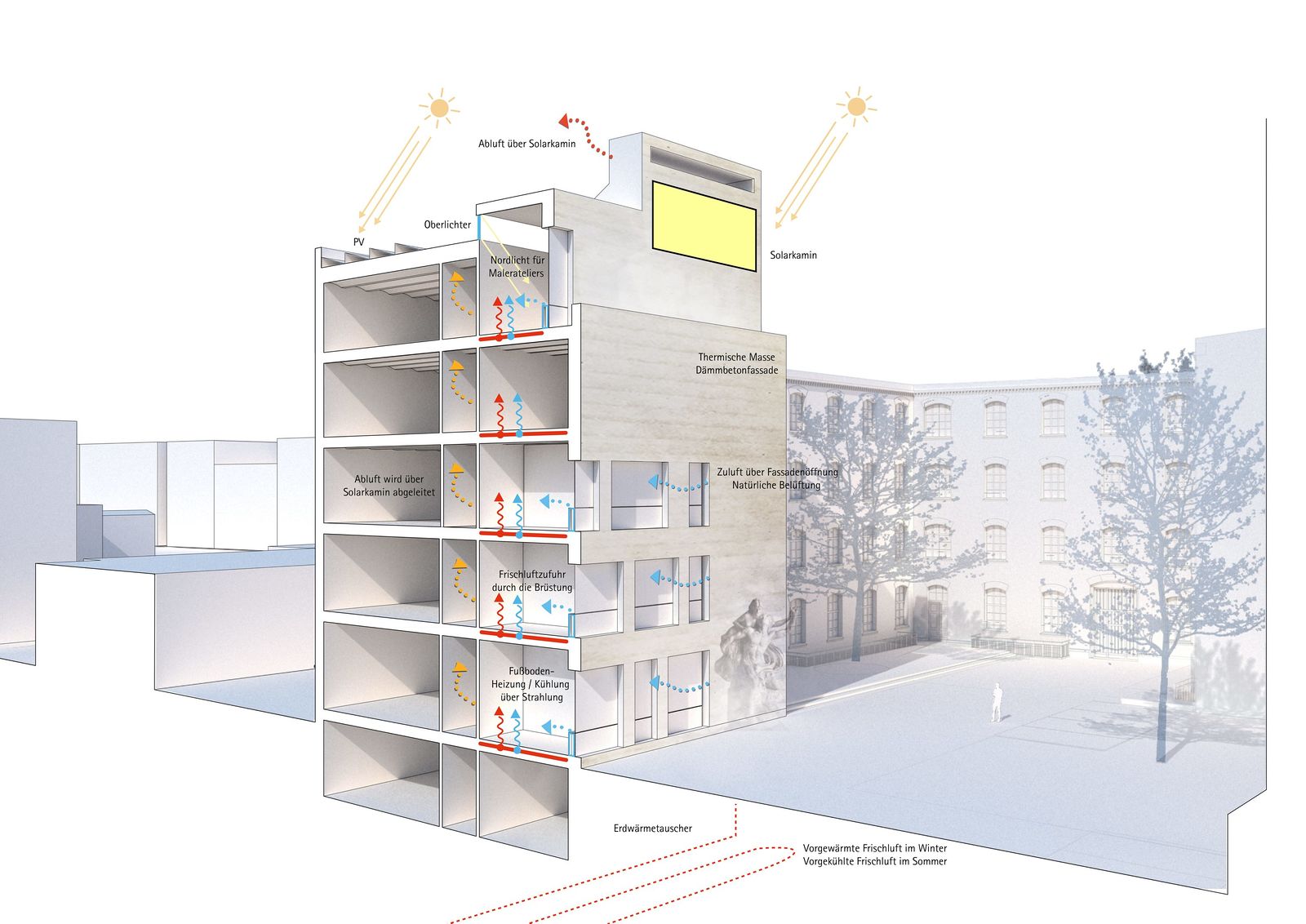
In reference to the core activities of the plaster casting facility, the facade is constructed using ultra-lightweight concrete panels – molded and cured material is used to create a new building sculpture.